A turbine, is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. A turbine is a turbomachine with at least one moving part called a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades
attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades so that they move and impart
rotational energy to the rotor.
Early turbine examples are windmills and waterwheels.
Gas, steam, and water
turbines have a casing around the blades that contains and controls the
working fluid. Credit for invention of the steam turbine is given both
to the British engineer Sir Charles Parsons (1854–1931), for invention of the reaction turbine and to Swedish engineer Gustaf de Laval (1845–1913), for invention of the impulse turbine. Modern steam turbines frequently employ both reaction and impulse in the same unit, typically varying the degree of reaction and impulse from the blade root to its periphery.
The word "turbine" was coined in 1822 by the French mining engineer Claude Burdin from the Latin turbo, or vortex, in a memoir, "Des turbines hydrauliques ou machines rotatoires à grande vitesse", which he submitted to the Académie royale des sciences in Paris. Benoit Fourneyron, a former student of Claude Burdin, built the first practical water turbine.
Operation theory

Schematic of impulse and reaction turbines, where the rotor is the rotating part, and the stator is the stationary part of the machine.
A working fluid contains potential energy (pressure head) and kinetic energy (velocity head). The fluid may be compressible or incompressible. Several physical principles are employed by turbines to collect this energy:
Impulse
turbines change the direction of flow of a high velocity fluid or gas
jet. The resulting impulse spins the turbine and leaves the fluid flow
with diminished kinetic energy. There is no pressure change of the fluid
or gas in the turbine blades
(the moving blades), as in the case of a steam or gas turbine, all the
pressure drop takes place in the stationary blades (the nozzles). Before
reaching the turbine, the fluid's pressure head is changed to velocity head by accelerating the fluid with a nozzle. Pelton wheels and de Laval turbines
use this process exclusively. Impulse turbines do not require a
pressure casement around the rotor since the fluid jet is created by the
nozzle prior to reaching the blades on the rotor. Newton's second law describes the transfer of energy for impulse turbines.
Reaction turbines develop torque
by reacting to the gas or fluid's pressure or mass. The pressure of the
gas or fluid changes as it passes through the turbine rotor blades. A
pressure casement is needed to contain the working fluid as it acts on
the turbine stage(s) or the turbine must be fully immersed in the fluid
flow (such as with wind turbines). The casing contains and directs the
working fluid and, for water turbines, maintains the suction imparted by
the draft tube. Francis turbines and most steam turbines
use this concept. For compressible working fluids, multiple turbine
stages are usually used to harness the expanding gas efficiently. Newton's third law describes the transfer of energy for reaction turbines.
In the case of steam turbines, such as would be used for marine
applications or for land-based electricity generation, a Parsons type
reaction turbine would require approximately double the number of blade
rows as a de Laval type impulse turbine, for the same degree of thermal
energy conversion. Whilst this makes the Parsons turbine much longer and
heavier, the overall efficiency of a reaction turbine is slightly
higher than the equivalent impulse turbine for the same thermal energy
conversion.
In practice, modern turbine designs use both reaction and impulse concepts to varying degrees whenever possible. Wind turbines use an airfoil to generate a reaction lift
from the moving fluid and impart it to the rotor. Wind turbines also
gain some energy from the impulse of the wind, by deflecting it at an
angle. Turbines with multiple stages may utilize either reaction or
impulse blading at high pressure. Steam turbines were traditionally more
impulse but continue to move towards reaction designs similar to those
used in gas turbines. At low pressure the operating fluid medium expands
in volume for small reductions in pressure. Under these conditions,
blading becomes strictly a reaction type design with the base of the
blade solely impulse. The reason is due to the effect of the rotation
speed for each blade. As the volume increases, the blade height
increases, and the base of the blade spins at a slower speed relative to
the tip. This change in speed forces a designer to change from impulse
at the base, to a high reaction style tip.
Classical turbine design methods were developed in the mid 19th
century. Vector analysis related the fluid flow with turbine shape and
rotation. Graphical calculation methods were used at first. Formulae for
the basic dimensions of turbine parts are well documented and a highly
efficient machine can be reliably designed for any fluid flow condition. Some of the calculations are empirical or 'rule of thumb' formulae, and others are based on classical mechanics. As with most engineering calculations, simplifying assumptions were made.
Velocity triangles
can be used to calculate the basic performance of a turbine stage. Gas
exits the stationary turbine nozzle guide vanes at absolute velocity Va1. The rotor rotates at velocity U. Relative to the rotor, the velocity of the gas as it impinges on the rotor entrance is Vr1. The gas is turned by the rotor and exits, relative to the rotor, at velocity Vr2. However, in absolute terms the rotor exit velocity is Va2.
The velocity triangles are constructed using these various velocity
vectors. Velocity triangles can be constructed at any section through
the blading (for example: hub, tip, midsection and so on) but are
usually shown at the mean stage radius. Mean performance for the stage
can be calculated from the velocity triangles, at this radius, using the
Euler equation:
Hence:
where:
 specific enthalpy drop across stage
specific enthalpy drop across stage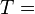 turbine entry total (or stagnation) temperature
turbine entry total (or stagnation) temperature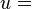 turbine rotor peripheral velocity
turbine rotor peripheral velocity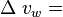 change in whirl velocity
change in whirl velocity
The turbine pressure ratio is a function of  and the turbine efficiency.
and the turbine efficiency.
 and the turbine efficiency.
and the turbine efficiency.
Modern turbine design carries the calculations further. Computational fluid dynamics
dispenses with many of the simplifying assumptions used to derive
classical formulas and computer software facilitates optimization. These
tools have led to steady improvements in turbine design over the last
forty years.
The primary numerical classification of a turbine is its specific speed.
This number describes the speed of the turbine at its maximum
efficiency with respect to the power and flow rate. The specific speed
is derived to be independent of turbine size. Given the fluid flow
conditions and the desired shaft output speed, the specific speed can be
calculated and an appropriate turbine design selected.
The specific speed, along with some fundamental formulas can be used
to reliably scale an existing design of known performance to a new size
with corresponding performance.
Off-design performance is normally displayed as a turbine map or characteristic.
Types
- Steam turbines are used for the generation of electricity in thermal power plants, such as plants using coal, fuel oil or nuclear fuel. They were once used to directly drive mechanical devices such as ships' propellers (for example the Turbinia, the first turbine-powered steam launch, )
but most such applications now use reduction gears or an intermediate
electrical step, where the turbine is used to generate electricity,
which then powers an electric motor
connected to the mechanical load. Turbo electric ship machinery was
particularly popular in the period immediately before and during World War II, primarily due to a lack of sufficient gear-cutting facilities in US and UK shipyards.
- Gas turbines
are sometimes referred to as turbine engines. Such engines usually
feature an inlet, fan, compressor, combustor and nozzle (possibly other
assemblies) in addition to one or more turbines.
- Transonic
turbine. The gas flow in most turbines employed in gas turbine engines
remains subsonic throughout the expansion process. In a transonic
turbine the gas flow becomes supersonic as it exits the nozzle guide
vanes, although the downstream velocities normally become subsonic.
Transonic turbines operate at a higher pressure ratio than normal but
are usually less efficient and uncommon.
- Contra-rotating turbines. With axial turbines,
some efficiency advantage can be obtained if a downstream turbine
rotates in the opposite direction to an upstream unit. However, the
complication can be counter-productive. A contra-rotating steam turbine,
usually known as the Ljungström turbine, was originally invented by
Swedish Engineer Fredrik Ljungström
(1875–1964) in Stockholm, and in partnership with his brother Birger
Ljungström he obtained a patent in 1894. The design is essentially a
multi-stage radial turbine
(or pair of 'nested' turbine rotors) offering great efficiency, four
times as large heat drop per stage as in the reaction (Parsons) turbine,
extremely compact design and the type met particular success in
backpressure power plants. However, contrary to other designs, large
steam volumes are handled with difficulty and only a combination with
axial flow turbines (DUREX) admits the turbine to be built for power
greater than ca 50 MW. In marine applications only about 50
turbo-electric units were ordered (of which a considerable amount were
finally sold to land plants) during 1917-19, and during 1920-22 a few
turbo-mechanic not very successful units were sold.
Only a few turbo-electric marine plants were still in use in the late
1960s (ss Ragne, ss Regin) while most land plants remain in use 2010.
- Statorless
turbine. Multi-stage turbines have a set of static (meaning stationary)
inlet guide vanes that direct the gasflow onto the rotating rotor
blades. In a statorless turbine the gasflow exiting an upstream rotor
impinges onto a downstream rotor without an intermediate set of stator
vanes (that rearrange the pressure/velocity energy levels of the flow)
being encountered.
- Ceramic
turbine. Conventional high-pressure turbine blades (and vanes) are made
from nickel based alloys and often utilise intricate internal
air-cooling passages to prevent the metal from overheating. In recent
years, experimental ceramic blades have been manufactured and tested in
gas turbines, with a view to increasing rotor inlet temperatures and/or,
possibly, eliminating aircooling. Ceramic blades are more brittle than
their metallic counterparts, and carry a greater risk of catastrophic
blade failure. This has tended to limit their use in jet engines and gas
turbines to the stator (stationary) blades.
- Shrouded
turbine. Many turbine rotor blades have shrouding at the top, which
interlocks with that of adjacent blades, to increase damping and thereby
reduce blade flutter. In large land-based electricity generation steam
turbines, the shrouding is often complemented, especially in the long
blades of a low-pressure turbine, with lacing wires. These wires pass
through holes drilled in the blades at suitable distances from the blade
root and are usually brazed to the blades at the point where they pass
through. Lacing wires reduce blade flutter in the central part of the
blades. The introduction of lacing wires substantially reduces the
instances of blade failure in large or low-pressure turbines.
- Shroudless turbine. Modern practice is, wherever possible, to eliminate the rotor shrouding, thus reducing the centrifugal load on the blade and the cooling requirements.
- Bladeless turbine uses the boundary layer effect and not a fluid impinging upon the blades as in a conventional turbine.
- Water turbines
- Pelton turbine, a type of impulse water turbine.
- Francis turbine, a type of widely used water turbine.
- Kaplan turbine, a variation of the Francis Turbine.
- Turgo turbine, a modified form of the Pelton wheel.
- Cross-flow turbine, also known as Banki-Michell turbine, or Ossberger turbine.
- Wind turbine. These normally operate as a single stage without nozzle and interstage guide vanes. An exception is the Éolienne Bollée, which has a stator and a rotor.
- Velocity compound "Curtis". Curtis combined the de Laval and Parsons
turbine by using a set of fixed nozzles on the first stage or stator
and then a rank of fixed and rotating blade rows, as in the Parsons or
de Laval, typically up to ten compared with up to a hundred stages of a
Parsons design. The overall efficiency of a Curtis design is less than
that of either the Parsons or de Laval designs, but it can be
satisfactorily operated through a much wider range of speeds, including
successful operation at low speeds and at lower pressures, which made it
ideal for use in ships' powerplant. In a Curtis arrangement, the entire
heat drop in the steam takes place in the initial nozzle row and both
the subsequent moving blade rows and stationary blade rows merely change
the direction of the steam. Use of a small section of a Curtis
arrangement, typically one nozzle section and two or three rows of
moving blades, is usually termed a Curtis 'Wheel' and in this form, the
Curtis found widespread use at sea as a 'governing stage' on many
reaction and impulse turbines and turbine sets. This practice is still
commonplace today in marine steam plant.
- Pressure compound multistage impulse, or "Rateau", after its French inventor, fr:Auguste Rateau.
The Rateau employs simple impulse rotors separated by a nozzle
diaphragm. The diaphragm is essentially a partition wall in the turbine
with a series of tunnels cut into it, funnel shaped with the broad end
facing the previous stage and the narrow the next they are also angled
to direct the steam jets onto the impulse rotor.
- Mercury vapour turbines used mercury as the working fluid, to improve the efficiency of fossil-fueled generating stations. Although a few power plants were built with combined mercury vapour and conventional steam turbines, the toxicity of the metal mercury was quickly apparent.
Uses
Almost all electrical power
on Earth is generated with a turbine of some type. Very high efficiency
steam turbines harness around 40% of the thermal energy, with the rest
exhausted as waste heat.
Most jet engines rely on turbines to supply mechanical work from their working fluid and fuel as do all nuclear ships and power plants.
Turbines are often part of a larger machine. A gas turbine,
for example, may refer to an internal combustion machine that contains a
turbine, ducts, compressor, combustor, heat-exchanger, fan and (in the
case of one designed to produce electricity) an alternator. Combustion
turbines and steam turbines may be connected to machinery such as pumps
and compressors, or may be used for propulsion of ships, usually through
an intermediate gearbox to reduce rotary speed.
Reciprocating piston engines such as aircraft engines can use a turbine powered by their exhaust to drive an intake-air compressor, a configuration known as a turbocharger (turbine supercharger) or, colloquially, a "turbo".
Turbines can have very high power density (i.e. the ratio of power to
weight, or power to volume). This is because of their ability to
operate at very high speeds. The Space Shuttle's main engines used turbopumps
(machines consisting of a pump driven by a turbine engine) to feed the
propellants (liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen) into the engine's
combustion chamber. The liquid hydrogen turbopump is slightly larger
than an automobile engine (weighing approximately 700 lb) and produces
nearly 70,000 hp (52.2 MW).
Turboexpanders are widely used as sources of refrigeration in industrial processes.
Military jet engines, as a branch of gas turbines, have recently been
used as primary flight controller in post-stall flight using jet
deflections that are also called thrust vectoring. The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration has also conducted a study about civilizing such thrust vectoring systems to recover jetliners from catastrophes.


கருத்துகள் இல்லை:
கருத்துரையிடுக